Explore Confucius’s Disciples in
5 Minutes
Confucius advocated the educational philosophy of “teaching without discrimination” and taught more than 3,000 students in his lifetime.
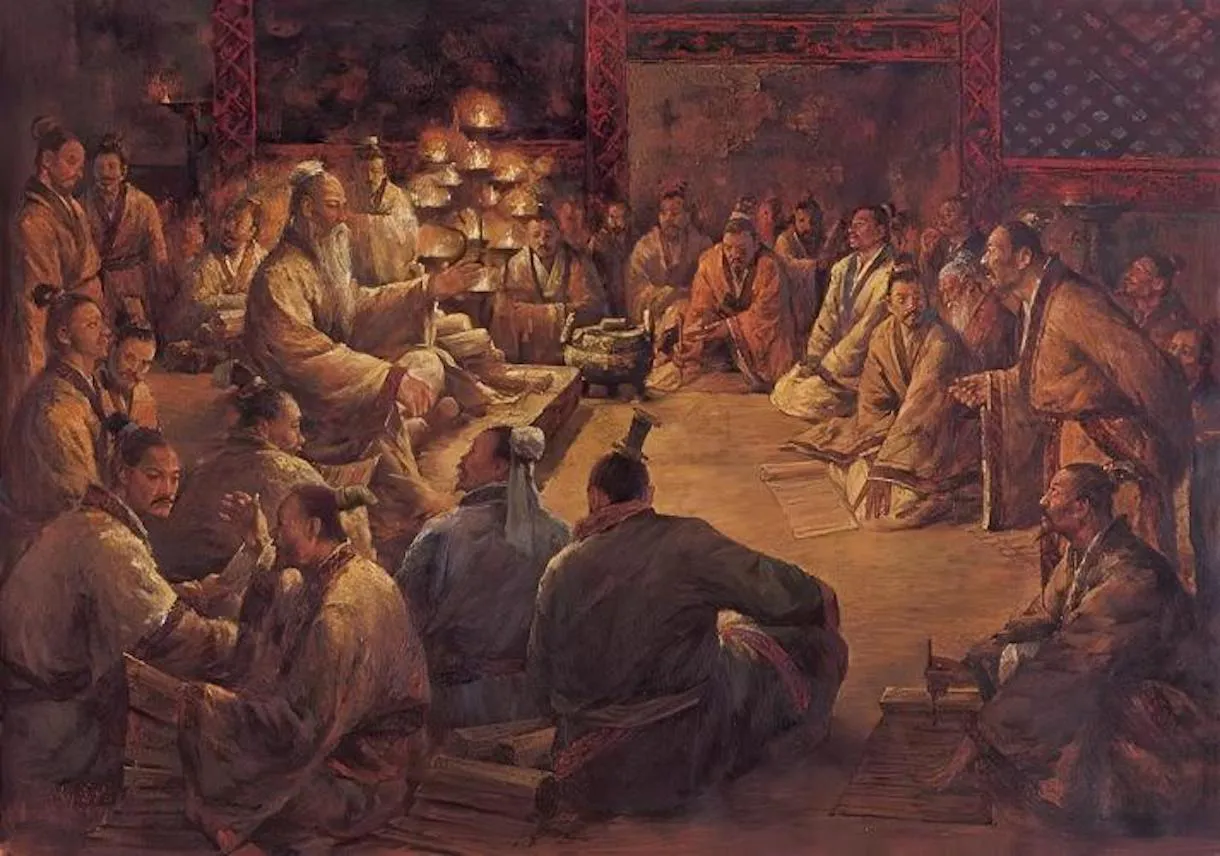

Confucius is an outstanding thinker and educator. He proposed and practiced the educational philosophy of “teaching without discrimination,” broke the monopoly of the nobility and the royal family on the education system, and pioneered private education.
He advocated “teaching according to aptitude” and cultivated numerous disciples throughout his life. According to The Confucian School’s Analects and other ancient records, Confucius taught over 3000 students. Over 70 of these students have performed excellently and made great achievements in various fields.
Therefore, later historical materials praise Confucius and his students. For instance, “Seventy-two Wise Men of Confucius” in Records of the Grand Historian: Confucius family and “The Ten Philosophers of Confucius” in The Analects of Confucius: Advanced mirror the high recognition of their talents and achievements.
Overview of Confucius’s Disciples
Confucius and his disciples were early Confucianism‘s most influential intellectuals and prototypes during the Spring and Autumn Period and the Warring States Period.
1. What are the Characteristics of Confucius’s Disciples?
Confucius began teaching at the age of 30. He did not judge his students by their rank or social status but recruited students from all walks of life and backgrounds with open-mindedness and compassion.
Confucius believed:
- Disciples who excelled in virtue: Yan Yuan (颜渊), Min Ziqian (闵子骞), Ran Boniu (冉伯牛), and Zhong Gong (仲弓).
- In speech: Zaiyu (宰予) and Zigong (子贡).
- In political affairs: Ran Qiu (冉求) and Jilu (季路).
- In literary affairs: Ziyou (子有) and Zixia (子夏).
These students represent the diversity and comprehensiveness of Confucius’s teaching. They have achieved excellence in character, eloquence, political ability, and literary talent. They have also made significant contributions to the transmission and development of Confucianism.

2. Where did Confucius’s Disciples Come From?
Confucius taught for more than 40 years and was followed by many students as he traveled. He had more than 3,000 disciples, but stories of only 70 of them have been recorded and passed down.
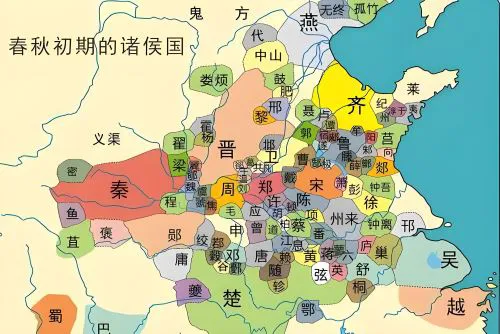
According to historical records, most of Confucius’s disciples came from his home country, the State of Lu(鲁), and many others came from other regions of China.
For example, six of them came from the region of Wey(卫) (e.g., Zigong), three from Qin(秦), two from Chen(陈) and Qi(齐), and one from Cai(蔡), Chu(楚), and Song(宋).
The diversity of his students’ backgrounds fully embodied Confucius’s educational philosophy: “All are equal in receiving education.”
3. Did Confucius Charge his Students Tuition Fees?
During the Spring and Autumn Periods, there was a traditional custom of paying homage to a teacher—”Shu Xiu” (an ancient gift of ten pieces of dried meat to honor a teacher, “束脩” in Chinese). Students were required to prepare a few gifts, usually ten strips of dried meat, to pay respect to the master.
Confucius regarded “Shu Xiu” as both a material gift and a spiritual commitment to study.
Confucius tended to take the students’ affordability into full consideration.
He usually charged a smaller amount of jerky for poorer students and sometimes even waived the entire fee.
It was considered a ritual donation for students from wealthy families, who often pay a sum commensurate with their wealth.

A Partial List of Confucius’s Disciples
Confucius cultivated many disciples in his life, but the names of less than 100 of them have been written down and preserved. This website organizes these names below according to the existing information.
| Serial No. | Name | Courtesy Name | Birth and Death | Native Place |
| 1 | 颜回 (Yan Hui) | 子渊 (Ziyuan, Yan Yuan) | 521–481 BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 2 | 闵损 (Min Sun) | 子骞 (Ziqian) | 536–487 BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 3 | 冉耕 (Ran Geng) | 伯牛 (Boniu) | 554–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 4 | 冉雍 (Ran Yong) | 仲弓 (Zhonggong) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 5 | 冉求 (Ran Qiu) | 子有 (Ziyou) | 522–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 6 | 仲由 (Zhong You) | 子路 (Zilu) | 542–480 BCE | 卞(Pian) |
| 7 | 宰予 (Zai Yu) | 子我 (Ziwo) | 522–458 BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 8 | 端木赐 (Duanmu Ci) | 子贡 (Zigong) | 520–456 BCE | 卫(Wey) |
| 9 | 言偃 (Yan Yan) | 子游 (Ziyou) | 506–443 BCE | 吴(Wu) |
| 10 | 卜商 (Bu Shang) | 子夏 (Zixia) | 507–400 BCE | 卫(Wey) |
| 11 | 颛孙师 (Zhuansun Shi) | 子张 (Zizhang) | 503–? BCE | 陈(Chen) |
| 12 | 曾参 (Zeng Shen) | 子舆 (Ziyu) | 505–435 BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 13 | 澹台灭明 (Tantai Mieming) | 子羽 (Ziyu) | 512–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 14 | 宓不齐 (Fu Buqi) | 子贱 (Zijian) | 521–445 BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 15 | 原宪 (Yuan Xian) | 子思 (Zisi) | 515–? BCE | 宋(Song) |
| 16 | 公冶长 (Gongye Chang) | 子长 (Zichang) | 519–470 BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 17 | 南宫括 (Nangong Kuo) | 子容 (Zirong) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 18 | 公晳哀 (Gongxi Ai) | 季次 (Jici) | 齐(Qi) | |
| 19 | 曾点 (Zeng Dian) | 子皙 (Zixi) | 546–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 20 | 颜无繇 (Yan Wuyou) | 路 (Lu) | 545–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 21 | 商瞿 (Shang Qu) | 子木 (Zimu) | 522–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 22 | 高柴 (Gao Chai) | 子羔 (Zigao) | 521–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 23 | 漆雕开 (Qidiao Kai) | 子开 (Zikai) | 540–489 BCE | 蔡(Cai) |
| 24 | 公伯缭 (Gongbo Liao) | 子周 (Zizhou) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 25 | 司马耕 (Sima Geng) | 子牛 (Ziniu) | 宋(Song) | |
| 26 | 樊须 (Fan Xu) | 子迟 (Zichi) | 鲁(Lu) / 齐(Qi) | |
| 27 | 有若 (You Ruo) | 子有 (Ziyou) | 508–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 28 | 公西赤 (Gongxi Chi) | 子华 (Zihua) | 509–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 29 | 巫马施 (Wuma Shi) | 子旗 (Ziqi) | 521–? BCE | 陈(Chen) |
| 30 | 梁鳣 (Liang Zhan) | 叔鱼 (Shuyu) | 522–440 BCE | 齐(Qi) |
| 31 | 颜幸 (Yan Xing) | 子柳 (Ziliu) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 32 | 冉孺 (Ran Ru) | 子鲁 (Zilu) | 501–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 33 | 曹恤 (Cao Xu) | 子循 (Zixun) | 501–? BCE | 蔡(Cai) |
| 34 | 伯虔 (Bo Qian) | 子析 (Zixi) | 501–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 35 | 公孙龙 (Gongsun Long) | 子石 (Zishi) | 498–? BCE | 楚(Chu) |
| 36 | 冉季 (Ran Ji) | 子产 (Zichan) | 498–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 37 | 公祖句兹 (Gongzu Gouzi) | 子之 (Zizhi) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 38 | 秦祖 (Qin Zu) | 子南 (Zinan) | 秦(Qin) | |
| 39 | 漆雕哆 (Qidiao Chi) | 子敛 (Zilian) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 40 | 颜高 (Yan Gao) | 子骄 (Zijiao) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 41 | 漆雕徒父 (Qidiao Dufu) | 子文 (Ziwen) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 42 | 壤驷赤 (Zeng Sichi) | 子徒 (Zitu) | 秦(Qin) | |
| 43 | 商泽 (Shang Zhai) | 子秀 (Zixiu) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 44 | 石作蜀 (ShiZuoShu) | 子明 (Ziming) | ||
| 45 | 任不齐 (Ren Buji) | 子选 (Zixuan) | 545–468 BCE | 薛(Xue) |
| 46 | 公良孺 (Gongliang Ru) | 子正 (Zizheng) | 陈(Chen) | |
| 47 | 后处 (Hou Chu) | 子里 (Zili) | 齐(Qi) | |
| 48 | 秦冉 (Qin Ran) | 开 (Kai) | 蔡(Cai) | |
| 49 | 公夏首 (Gongxia Shou) | 乘 (Sheng) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 50 | 奚容箴 (Xi Yongdian) | 子皙 (Zixi) | 卫(Wey) | |
| 51 | 公肩定 (Gong Jianding) | 子中 (Zizhong) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 52 | 颜祖 (Yan Zu) | 襄 (Xiang) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 53 | 鄡单 (Jiaodan) | 子家 (Zijia) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 54 | 句井疆 (Gou Jingjiang) | 子疆 (Zijiang) | 卫(Wey) | |
| 55 | 罕父黑 (Han fuhei) | 子索 (Zisuo) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 56 | 秦商 (Qin Shang) | 子丕 (Zipei) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 57 | 申党 (Shen Dang) | 周 (Zhou) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 58 | 颜之仆 (Yan Zhipo) | 子叔 (Zishu) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 59 | 荣旗 (Yong Qi) | 子祈 (Ziqi) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 60 | 县成 (Xian Chang) | 子祺 (Ziqi) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 61 | 左人郢 (Zuo Renying) | 行 (Xing) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 62 | 燕伋 (Yan Zhi) | 思 (Si) | 秦(Qin) | |
| 63 | 郑邦 (Zhang Bang) | 子徒 (Zitu) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 64 | 秦非 (Qin Fei) | 子之 (Zizhi) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 65 | 施之常 (Shi Zhichang) | 子恒 (Ziheng) | 546–? BCE | 鲁(Lu) |
| 66 | 颜哙 (Yan Kuai) | 子声 (Zisheng) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 67 | 步叔乘 (Bu Shusheng) | 子车 (Ziche) | 齐(Qi) | |
| 68 | 原亢籍 (Yuan kangji) | 籍 (Ji) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 69 | 乐欬 (Yue Ke) | 子声 (Zisheng) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 70 | 廉絜 (Lian Jie) | 庸 (Yong) | 卫(Wey) | |
| 71 | 叔仲会 (Shuzhung Hui) | 子期 (Ziqi) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 72 | 颜何 (Yan He) | 冉 (Ran) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 73 | 狄黑 (Di Hei) | 皙 (Zhe) | 卫(Wey) | |
| 74 | 邦巽 (Kui Sun) | 子敛 (Zilian) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 75 | 孔忠 (Kong zhong) | 子蔑 (Zimie) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 76 | 公西舆如 (Gongxi Yuru) | 子上 (Zishang) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 77 | 陈亢 (Chan Kang) | 子亢 (Zikang) | 511–430 BCE | 陈(Chen) |
| 78 | 林放 (Lin Fang) | 子丘 (Ziqiu) | 鲁(Lu) | |
| 79 | 琴牢 (Qin Lao) | 子开 (Zikai) | 卫(Wey) | |
| 80 | 缪和 (Miao he) | |||
| 81 | 县亶 (Xian Dan) | 子象 (Zixiang) | 鲁(Lu) |
Controversies
There are many discrepancies between different records about Confucius’s disciples.
Therefore, it is necessary to treat different historical records with caution and consider them comprehensively in the study.
Some views are organized here for reference only:
- In The Collected Notes on The Analects of Confucius (论语集解), Confucius had 26 disciples, including He Yan (何晏).
- In Collected Annotations on The Analects of Confucius (论语集注), Zhu Xi (朱熹) recorded that Confucious has 27 disciples.
- In The Interpretation of Analects of Confucius (论语译注), 24 people are labeled as disciples of Confucius.
- According to Biographies (列传), 27 people are mentioned in Analects of Confucius. It is uncertain whether Shen Dang (申党) and Yuan Kangji (原亢籍) are included in the 27 people. If they are not included, there are 29 disciples of Confucius.
- In The Analects of Confucius, there is a chapter titled Explanation of the Seventy-two Disciples, so Confucius may have 72 disciples. Among them, 26 of them are mentioned in The Analects of Confucius.
FAQs
Yan Hui is the best and favoriate disciple of Confucius. He is a learned man who strictly followed the concepts of Ren and Li advocated by Confucius, and he is also known as the Sage of Restoration in later times.
According to historical records, Confucius taught for more than 40 years and taught a total of over 3,000 students.
According to various history books, there were 72 famous disciples of Confucius. The ten best among them are Yan Hui (Zi Yuan), Min Sun (Zi Qian), Ran Geng (Bo Niu), Ran Yong (Zhong Gong), Ran Qiu (Zi You), Zhong You (Zi Lu), Zai Yu (Zi Wo), Duanmu Ci (Zi Gong), Yan Yan (Zi You), Bu Shang (Zi Xia).
The main teaching content of Confucius covered three areas, namely, moral education, cultural knowledge and skill development.
No, Mencius is not a student of Confucius. Confucius lived during the Spring and Autumn Period, while Mencius lived during the Warring States Period. Mencius inherited and developed Confucianism, and he was honored as “the Second Sage” (亚圣, only secondary to Confucius).
No.
Although Confucius advocated teaching without discrimination, there is no relevant historical record of female students of Confucius, which reflects the limitations of that time.
